Travel is the oldest human activity that, from the very first wish to satisfy only one straightforward need to move to live this proved an incredibly simple way towards the multifaceted method to enjoy leisure, trade, discovery, and cultural exchange. The knowledge of how it all had been through history, struggles, and how far we have traveled from where we could have been, changes the lives of many people, influenced their civilization, and their economy to reach where we are today in the world of these changing times.
Travel History as a Necessity of Survival: Early days
Thus, traveling history was much more of a compulsion during prehistoric times. Early man, being a wanderer, traveled for food, water, and more friendly climatic conditions. Tools, fire, and primitive apparel enabled early man to roam around more areas, thus gradually moving from the hunter-gatherer cycle to the agricultural cycle. It was no pleasure journey; rather, it was a flight for survival.

Rivers, mountains, and other geographical features may have been the routes that those people later started to follow to pave their way in migrating the earth for propagation purposes and to all continents from Africa.
Rise of Civilization and First Trade Routes
About 10,000 years ago, agriculture history started to provide a relatively sedentary framework for human populations but was still based on travel to exchange goods. Once regional differences uniquely started to emerge, man felt the need to devise ways of exchanging such values. This is one of the aspects that led to some of the earliest trade routes.
The second of the ancient but very well known is the Silk Route tracing back its history to the Han Dynasty of China 130 BCE. An infrastructure that began in the Mediterranean linking China by mutual trading of goods of which there was silk, spices, precious stones, and other treasured goods beside material trade it opened up a door for the exchange of culture, religion, and technology.
This route, the Incense Route, linked up the Arabian Peninsula to the Mediterranean and Egypt for the carriage of rich spices and incense. However, the Amber Route brought Northern Europe to the Mediterranean for access to the most prized resin used for jewelry and art.
Exploration the History in ancient times
Beyond the timeline of social development, there was also the other third that needed to be explored to the other end. Amongst some of the oldest recorded expeditions were a touring agreement traceable back to ancient Egyptian, Phoenician, and Greek persons.
Egyptian Expeditions: A Pharaoh of Egypt, around 1500 BCE had prepared the other countries’ expeditions that she intended, including Punt, which is now Somalia to try to establish trade relations and to reach even further distances in foreign countries. Most of those were a mix of trading and diplomacy missions.

Phoenician Mariners: These are the Phoenicians, an ancient Semitic people. They were world-class mariners. They roamed through the Mediterranean Sea building colonies history and trading posts around it. From that experience in navigation, they ventured and traded as far away as Britain and West Africa.
Greek Exploration: Intellectual explorers discover new lands with which the ancient Greeks are associated. Because of the oldest histories of travel writings that had survived into their day, such as Herodotus and Pausanias, authors, Alexander the Great exposed vast new lands to Greek culture, language, and trade when he took his campaigns east to India in 323 BCE.
Roman Empire and Road Building
What do we know about road networks that made it possible to travel and, by implication, to trade across Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa? The Romans built many roads; today, most of them are still in use. These roads were one of the most important ingredients for the mobility of armies, trade goods, and information across the empire.

So many reasons forced the Romans to travel, and such include commerce and military campaigns, embassies, as well as tourism history. The wealthy Romans used their holidays in seashore resorts such as Baiae. This is a resort town of the Bay of Naples and so known for its well-equipped villas and hot springs.
The Great Word is “All roads lead to Rome presses the issue that after all Rome emerged to be the center of the ancient world with an infrastructure designed to cross the entire empire. Travel was quite safe in Roman times because that time had Pax Romana-the period of more than two centuries-duration which peace and stability had prevailed.
Medieval Period: Pilgrimage and Exploration of Travel History
It proved only what would now be known as the European Dark Ages when the curtain of European civilization came down with the fall of the Roman Empire in 476 CE but at no stage proved it to be the end of travel that found its way religiously, commercially, or exploratively in the medieval period.
Religious tourism history was one of the huge issues that transcended the Christian and Muslim worlds. Pilgrims found holy pilgrimage sites everywhere, to Mecca, and Santiago de Compostela. Routes Camino de Santiago from Spain for example lifelines of spiritual devotion, trade, and culture exchange.

The discovery and settlement of lands outside Europe, even before the continent became part of Europe, was already done by the Vikings of North America during the 8th to the 11th century. Longships easily reached the farthest places, which they did, reaching up to present-day Canada before other Europeans.
Exploration and Islamic history: Explorers, scholars, and merchants traveled thousands of miles in the Golden Age of Islam. This refers to the period between the 8th and the 14th century. Nominally, the most famous explorer of the age would be the traveler of the 14th century; who covered over 75,000 miles within Africa, the Middle East, India, and China specifically Ibn Battuta.
Age of Exploration: Expand Horizons
This is the starting point, corresponding to the late 15th century, for a quest by European powers to find a new route to trade and a new land age of discovery that had begun through voyages that went on to revolutionize the world’s understanding of geography and its interconnectedness.
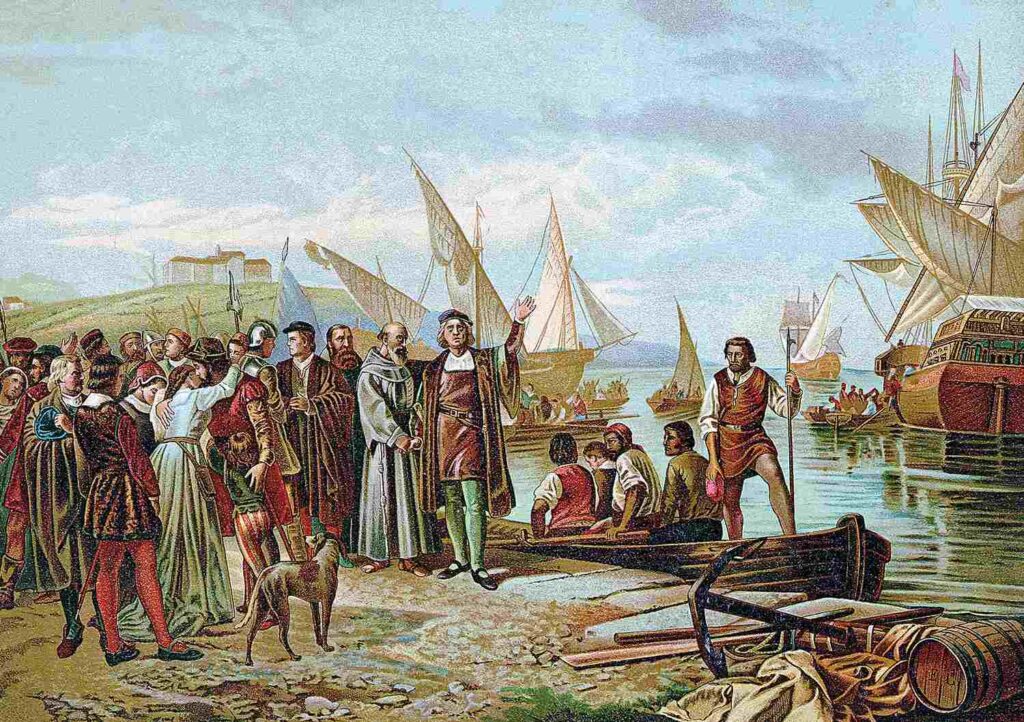
He was on a voyage from Spain to the American continent. Christopher Columbus was supported by Spain to fund an expedition to the west. He was in search of a new route to India. He opened up the New World for European exploration and colonization although what he sought was a westward route to India.

Vasco da Gama: 1498-da Gama was the first European to reach India over the sea crossing around the Southern tip of Africa marking a new shift in global trade as new routes had opened up in seas.
Ferdinand Magellan: 1519 to 1522 He was the first man to cross the world. He proved that the earth is round and that all waters are interconnected. Yet, he died himself as he brought his crew back to Spain after centuries because his travel history changed the world into a new turn.
Discoveries of the New World
This age of exploration led to untold riches and power for empires in Europe, but it went along with an unprecedented scale of cross-cultural diffusion and brought an unprecedented scale of disaster to the indigenous populations during the time of discovery.
Industrial Revolution Travel History
Industrialization was the greatest change travel has experienced since it started almost in every sense, although the real consequences of the process of industrialization came in the 18th and 19th centuries. Steam trains and later on automobiles brought about a possibility that, so far, traveling men were hard to imagine: easy but not dangerous travel; quick but not slow.
It revolutionized travel in the first two decades of the 19th century when travel by rail was permitted. In 1825 it was the world’s first railway ever constructed which entered service carrying passengers-the Stockton and Darlington Railway in England. Now men could travel farther, far more comfortably than ever before. That created tourism.

Steamships: Marine travel, now began to depend solely on steamships and it soon became smoother and faster with the arrival of this powerful machinery. The first iron-hulled, steam-powered passenger steamer was constructed in 1843, SS Great Britain, as an engineering wonder that was to change the way crossing the Atlantic would be done, thus cutting down on travel time from Europe to America crossing the Atlantic.
Cars were actually invented at the end of the 19th century, but they promised the unbridled freedom of movement to humankind. It was only then with Henry Ford’s Model T as well as with the coming in of the production lines at the turn of the 20th century that cars were mass-produced; thus, made accessible to the masses, opening the door to personal travel and the first wave of the road trip.
Tourism Boom
The other mass tourism was also a result of the 19th century. Like the former, it too was attributed to the revolutionary imagination of Thomas Cook, an enterprising British entrepreneur, who, in 1841 designed the first packaged tour. The tours designed by Cook were among the first ways travel became an ‘affordable luxury’ for an emerging middle class since, during that time when those tours were designed, traveling had already become an ‘affordable luxury’.

He was the first to follow the policy of a group tour, designed and established for the tourism practices of modern times. It remained in the pockets of the rich-elites-more especially British by the end of the 19th century by the Grand Tour or long journey through Europe, Thomas Cook & Son eventually became an enormous international travel business that provided transport as well as accommodation services.
The 20th Century: The Golden Age of Air Travel History
Air travel started during the initial decades of the 20th century when directions of travel began changing in all parts of the world. It was in the year 1903 when the Wright brothers were making their first powered flight. The early years that were marked for commercial aviation to resume their functionalities in those regions began.
It was, however, only in 1914 that air travel became part of the mass mainstream when the first commercial flight came into use. It required a war after the last war to get people used to traveling in the air. It was only then that the first commercial jet engines of the 1950s laid down that ground upon which mass commercial air travel could be faster, safer, and even more efficient. Other early innovators in overseas travel are Pan Am and BOAC, now British Airways.
The Jet Age: This has been sometimes referred to as the Golden Age of Air Travel because it had that glamour attached to it. Vast cabins and luxurious services, coupled with the glamour attached to flying itself, were a part of this service. Competition by airlines that offered the best experience made the flight a status symbol and an icon of modernity.
Digital Age: Traveling History in the 21st Century
The modern one, compared to the former, is more democratized since the factors limiting traveling are not merely a few rich people roaming all over the globe. The online has democratized and altered every perspective through which one would plan and make bookings for his or her travel. Budget airlines- were in line with the emergence of Airbnb accommodation to make it cheaper and accessible to millions of people around the globe.
Planning and comparing booking a trip can be pretty easy using platforms like Expedia, Booking.com, or simply TripAdvisor. Travel History has become super shareable, and picture-driven as well with companies like Instagram and the large number of travel blogs that eventually impact destinations.

Low-cost carrier: Boundary-less brand diffusion of Ryanair and Southwest Airlines allows a chap from the street to fly beyond his doorstep and further away than he ever would have dreamed-to distant places at a fraction of the price of getting there.
Travel and Sustainability: With the awakened conscience of the world about the issues with climate change, decisions regarding how to make traveling sustainable would increase as well. From that up to the present, we have ecotourism and slow travel, which are as low as they can go on their impacts on the environment and then merge eventually with the local cultures.
FAQS of History of Travel
1. When did traveling start?
This would be the first phase where a human would travel for his survival demands such as food, shelter, and so many life conditions. Still, the highly structured movement was linked to objectives such as trade, exploration, or religious places due to the emergence of the ancient civilization.
2. Some of the oldest notable historical trade routes?
Other such long trade routes with historical periods that date back centuries past are the Silk Route that connects China to the Mediterranean and the Incense Route linking the Arabian Peninsula with Egypt, with the Mediterranean. These routes also were used to exchange goods along with other cultures and ideas.
3. Who are the first explorers in history?
For instance, Ibn Battuta had crossed a greater part of Africa and a vast portion of the Middle East and Asia. Marco Polo had passed over from Venice to China in the 13th century. Even legends highlight that another Viking explorer known as Leif Erikson had traversed North America before the year 1000. Those heroes make travel History Vast.
4. What is there in the ancient Roman Empire that makes it add up to the world of travel?
They constructed a massive system of roads throughout Europe, the Near East, and North Africa. They had roads connecting the empire, so it was pretty easy to move armies, merchants, and travelers around the empire.
5. How did the Age of Exploration alter the way people anywhere in the world moved around?
This was during the Age of Exploration that opened up the known world from the 15th century up to the 17th century. This, therefore, paved the way for trade routes as well as the colonization of new lands between Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
6. Which era in history is generally considered the birth of modern tourism?
Modern tourism began in the early 19th century. However, it was Thomas Cook who invented the package tour since he made traveling easier for the new middle class and Became a great personality in the history of tourism.
7. For how long have people traveled by air?
But then, of course, came the boom in air travel in the 1950s with the entry of commercial jetliners following World War II. So, in that sense, this period is basically called the age of glamour and advancement in aircraft designs: the Jet Age which was established in the 1960s and 1970s.
8. Impacts of Technology on travel history?
The internet-based travel agencies have made this aspect easier and more simplified in terms of planning and booking. Social media has also dictated trends meant to be considered in traveling. Budget airlines have made traveling internationally cheaper.
9. What is sustainable travel history?
In other words, sustainable travel is a type of travel with a sound practice reducing impacts both to the environment and local communities where a person travels. These include a low carbon footprint, environment-friendly accommodations, and a movement towards cultural preservation.
10. What is the Future of Travel History?
Of course, the most likely forms for expected movements shortly would include innovation in technology, a thrust towards sustainability, and an evolving passenger profile. Virtual reality-pre-travel experiences might be something relevant to that concept – the very same thing to be increasingly related and addressed with regard to best practices in ecotourism and sustainability.
Conclusion
Indeed, the travels in the history of man are rather interesting in showing the different standards that history has to offer in terms of man’s evolution from mere survival-driven migration to the kind of adventure of today: globetrotting. Each has its marks and contribution to the rich tapestry of human culture and understanding. Be it for trade, exploration, pilgrimage, or just for leisure, travel history has always been a bridge interlinking people, places, and ideas.






